High-throughput microrespirometric characterization of activated sludge inhibition by silver nanoparticles†
Abstract
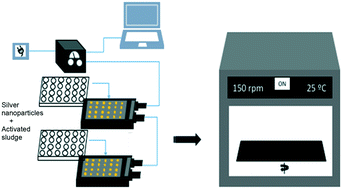
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are widely used in a high number of industrial applications and are becoming prevalent in wastewater effluents. It is known that AgNPs exert a toxic effect on activated sludge processes, but to what extent and under which conditions are still largely unknown. The inhibitory effect of AgNPs on a synthetic wastewater treatment process was tested using pulse microrespirometry (i.e., a pulse of substrate is injected into a microreactor system). Several conditions were tested, including AgNP concentration, substrate to biomass ratio (S0/X0) and exposure time. The inhibitory effects were quantified through the percentage of inhibition of the exogenous and endogenous respiration rates as well as through determination of the half saturation constant (KS), inhibition constant (KI) and maximum oxygen uptake rate (OURmax). The results indicated that AgNPs exert uncompetitive inhibition and the concentration that caused a 50% of inhibition (IC50) of the exogenous respiration rate was 3.32 ± 0.16 mg L−1. The inhibitory effect of AgNPs on the endogenous respiration was relatively lower, with an IC50 of 7.12 ± 0.11 mg L−1. Overall, it was observed that an increase in the S0/X0 ratio resulted in higher inhibition and that the inhibitory effects of AgNPs decreased with exposure time.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...