Cellular response of Chlorella pyrenoidosa to oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes†
Abstract
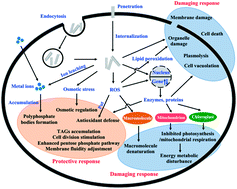
Although many reports have demonstrated significant toxicity upon exposure to carbon nanotubes (CNTs), the interaction of these materials with microalgae and the resulting physiological responses are largely unknown. This study investigated the interaction between oxidized multi-walled CNTs (o-MWCNTs) and algal cells (Chlorella pyrenoidosa), with a focus on assessing CNT cellular internalization as well as physiological and molecular responses to exposure. The results show that o-MWCNTs exhibited greater algal toxicity than pristine MWCNTs and that the acute toxicity was positively correlated with the oxidation level of the o-MWCNTs. This enhanced acute toxicity was closely related to the greater agglomeration of o-MWCNTs with algal cells. CNT attachment to the cell surface facilitated internalization by direct penetration and by endocytosis. Algal cells experienced increased antioxidant defense upon CNT exposure/stress. Additional cellular responses included regulation of cell membrane fluidity and osmotic pressure, formation of polyphosphate bodies, accumulation of neutral lipids, and stimulation of cell division and the pentose phosphate pathway. When the protective responses were exhausted, toxicity in the form of membrane and organelle damage, denaturation of macromolecules, and metabolic disturbance occurred, resulting in compromised cell integrity and eventual death. The findings of this work provide new insights useful for understanding the fate and toxicity of CNTs in aquatic environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...