Stabilizing interaction of exopolymers with nano-Se and impact on mercury immobilization in soil and groundwater†
Abstract
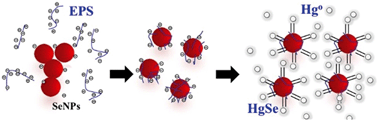
Remediation of metal-contaminated soils and waters using nanoparticles is highly limited by their strong tendency to aggregate in soil solution and natural water. In order to enhance the remediation of Hg0-contaminated soil solution and groundwater by Se nanoparticles (SeNPs), the effects of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the stability of SeNPs and Hg0 removal were investigated. EPS from the selenite-reducing bacterium Citrobacter freundii Y9 were found to make SeNPs more negatively charged by strong adsorption, which significantly enhanced the stability of SeNPs. The protein, carboxylate, polysaccharide and lipid components of the EPS were involved in the adsorption to SeNPs. Fluorescence quenching titration measurements implied that the binding of proteinaceous substances in the EPS to SeNPs was static quenching. EPS can therefore enhance the remediation efficiency of SeNPs for soil solution and groundwater contaminated with Hg0. This study highlights that bacterial EPS can be used as an effective natural dispersant for SeNPs, therefore improving the efficiency of mercury immobilization in contaminated waters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...