Electrochemical surface charge-inversion from semi-insulating Sb2Se3 photoanodes and abrupt photocurrent generation for water splitting†
Abstract
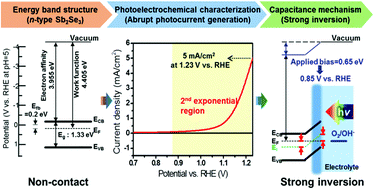
Binary chalcogenide Sb2Se3 shows dominantly p-type electrical conductivity and poor photocathodic performance; however, its narrow band gap and low work function suggest satisfactory conditions for the generation of the inversion state at the surface if used as a photoanode. We propose a fabrication design for the synthesis of n-type Sb2Se3 by suppressing the formation of antisite SbSe defects, where excessively thick Se layers deposited on the electrodeposited Sb–Se precursors and high N2 pressure are introduced during the annealing step. Surprisingly, the linear sweep voltage (LSV) measurement from the n-type Sb2Se3 shows remarkably enhanced photocurrent density (up to approximately 5 mA cm−2 at 1.23 V vs. a reversible hydrogen electrode) under light illumination, which is the highest performance among pristine binary photoelectrodes yet recorded. In addition, the LSV curve exhibits non-typical behavior with a significant increase of the photocurrent at the specific potential. The measured current density under light illumination and no dark current indicate a vigorous photoactive reaction from photogenerated carriers. Here, the abrupt increase in photocurrent density is attributed to the conduction path of hole carriers originating from the charge inversion state with p-type conductivity at the surface, allowing significant carrier injection into the electrolyte. Based on electrochemical analyses, the mechanism that results in outstanding photocurrent gain from the novel n-type Sb2Se3 photoanodes was proposed and their further development possibilities via additional improvements were presented.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...