Structural and thermodynamic stability of uranyl–deferiprone complexes and the removal efficacy of U(vi) at the cellular level†
Abstract
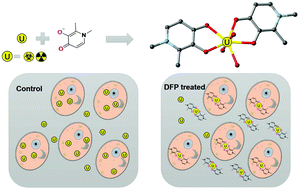
Deferiprone (3-hydroxy-1,2-dimethyl-4(1H)-pyridone, DFP), which is a drug clinically used for removing heavy metals in vivo, was explored for its removal efficiency towards uranium. The reaction of uranyl nitrate hexahydrate with DFP at room temperature yielded the compound [(UO2)(H2O)(C7NO2H8)2]·4H2O (1), which crystallizes from a mixed solution of methanol and water (pH = 7.0). X-ray diffraction shows that the stable complexation of uranyl occurs from the coordination of two bidentate DFP ligands perpendicular to the O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) U
U![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O unit with a fifth coordinating oxygen atom coming from one water molecule, resulting in a pentagonal bipyramidal geometry. The formation constants of uranyl and DFP complexes were measured and the species distribution diagram illustrates that UO2L2 (94.6%) is the dominant uranyl-DFP complex in 0.1 M KCl solution at physiological pH = 7.4. The results from both crystallographic and potentiometric studies imply that the metal : ligand ratio is 1 : 2. The effectiveness of using DFP to remove uranium was examined at the cellular level, and the results suggest that it can significantly reduce the cellular uptake and increase the cellular release of U(VI) in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (NRK-52E).
O unit with a fifth coordinating oxygen atom coming from one water molecule, resulting in a pentagonal bipyramidal geometry. The formation constants of uranyl and DFP complexes were measured and the species distribution diagram illustrates that UO2L2 (94.6%) is the dominant uranyl-DFP complex in 0.1 M KCl solution at physiological pH = 7.4. The results from both crystallographic and potentiometric studies imply that the metal : ligand ratio is 1 : 2. The effectiveness of using DFP to remove uranium was examined at the cellular level, and the results suggest that it can significantly reduce the cellular uptake and increase the cellular release of U(VI) in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (NRK-52E).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...