Green synthesis of balsam pear-shaped BiVO4/BiPO4 nanocomposite for degradation of organic dye and antibiotic metronidazole†
Abstract
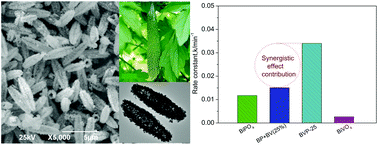
A novel BiVO4/BiPO4 composite with a balsam pear-shaped morphology was fabricated by a green hydrothermal synthesis approach, which didn't employ a strong acid and base, and neither a template or surfactant. The co-precipitation hydrothermal process had significant influence not only on particle size and shape, but also on the BiVO4 oriented growth along the (040) facet. The morphology, microstructure, light absorption and emission properties were analyzed by several characterization techniques. A formation mechanism for the hollow BiVO4/BiPO4 composite was proposed on the basis of time-dependent SEM observations. Charge transfer absorption and an efficient charge separation were observed by UV-vis DRS, PL spectra and photocurrent measurements, which suggest that there are chemical interactions between BiVO4 and BiPO4. The above synergistic effects of the as-prepared composite result in a higher photocatalytic performance for the degradation of RhB and MNZ compared with the single component and their physical mixture. Besides that, the special hollow structure and preferred exposure of the BiVO4 (040) facet could contribute to the dramatically improved performance. Subsequently, a possible photocatalytic mechanism over the BiVO4/BiPO4 composite was proposed based on experiment and theoretical analysis. These results indicate that the hollow BiVO4/BiPO4 composite has a great potential application value for the treatment of organic dyes and medicine wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...