Direct catalytic co-conversion of cellulose and methane to renewable petrochemicals†
Abstract
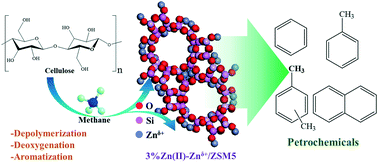
The catalytic co-conversion of cellulose and methane to aromatics was investigated over various Zn-containing zeolite catalysts. Higher aromatic yield (42.3% C) with BTEX selectivity of 70% and much lower solid residue yield (char: 9.45% C) are achieved over 3%Zn(II)–Znδ+/ZSM5 (0 < δ < 2) at 450 °C and 2.5 MPa. The loading of ZnO clusters or Zn2+ ions could be beneficial for the formation of aromatic products, and the introduction of Znδ+ species via CVD could improve BTEX selectivity and methane conversion. Co-feeding with methane inhibits the formation of coke or heavy substances and maximizes the carbon utilization efficiency for the formation of aromatics. Methane also enhances the oxygen removal efficiency to improve the quality of the liquid products. Methane participation in the formation of aromatic products is evidenced by liquid 1H, 2H and 13C NMR investigations, which reveal that methane tends to be incorporated into both the methyl group and the phenyl ring. The results of pyridine absorption and NH3-TPD indicate that the balanced distribution of Brønsted and Lewis acid sites and the appropriate ratio of weak to moderate acidic sites may benefit aromatic formation. XPS and XAS spectra of Zn species confirm the presence of Znδ+ species with oxygen vacancies, which show a higher selectivity for petrochemicals. The results reported in this work will give more insight into the catalytic chemistry of cellulose valorization under a methane environment and the design of rational catalysts for the cost-efficient utilization of biomass resources and natural gas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...