Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of iron nanoparticles as hydrogenation catalysts in alcohols and tetraalkylphosphonium ionic liquids: do solvents matter?
Abstract
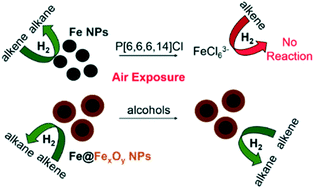
Iron nanoparticles (Fe NPs) synthesized via a one-pot chemical reduction strategy in neat alcohol or water/alcohol mixtures are compared to and contrasted with those synthesized in tetraalkylphosphonium ionic liquids with respect to their catalytic activities for the hydrogenation of simple olefins. It was observed that Fe NPs could catalyze the conversion of 2-norbornene to norbornane and 1-octene to octane in good yields under moderately high hydrogen pressures. Core–shell type Fe@FexOy particles in alcoholic solvents with larger sizes show greater resistance to catalytic deactivation after several reaction cycles, whereas halide ionic liquid-capped Fe particles show a marked tendency towards oxidative degradation, which limits their utility in catalysis unless rigorous anhydrous and anoxic conditions are maintained. Finally, in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy was applied to determine the fate of these systems upon catalysis and exposure to air. No change in Fe speciation was seen for Fe@FexOy nanoparticles in alcohol solvents. Fe nanoparticles in ionic liquids with strongly coordinating anions such as halides were not particularly stable to oxidation, while those in ionic liquids with non-coordinating anions agglomerate during catalysis, as well as undergoing slow oxidative degradation, thus making these systems less useful for catalysis compared to their counterparts in alcoholic solvents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...