Effects of graphitization of carbon nanospheres on hydrodeoxygenation activity of molybdenum carbide†
Abstract
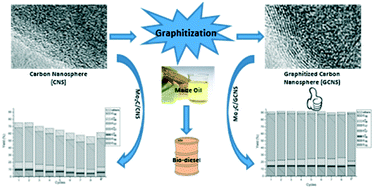
Cellulose-derived carbon materials were prepared and employed as supports for molybdenum carbide catalysts, and their catalytic activity for hydrodeoxygenation of maize oil was tested in an autoclave under different reaction conditions. Carbon nanospheres, which can be simply synthesized via hydrothermal carbonization and whose morphology can be easily controlled, were employed as supports to study the relationship between the graphitization degree of carbon supports and the hydrodeoxygenation activity of supported molybdenum carbide catalysts. Ferric chloride was employed as a graphitization reagent to modify the surface properties of the carbon nanospheres. Graphitized carbon nanosphere materials with appropriate FeCl3 to carbon ratios (1–50%) showed outstanding properties to work as supports for Mo2C catalysts. Suitable reaction conditions for comparing these catalysts were found out by testing carbon nanosphere supported Mo2C catalysts with different loadings (5–40%) at several temperatures (513–553 K) and initial hydrogen pressures (2.0–3.0 MPa). The best conversion and hydrocarbon yield they reached were 91.1% and 88.3%, which were 21% and 31% higher than the results from the ungraphitized carbon nanosphere supported catalyst under the same conditions, respectively. Cellulose-derived carbon materials might be competitive with carbon nanotubes as catalyst supports in the field of hydrodeoxygenation and maybe in other areas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...