Recyclable cobalt(0) nanoparticle catalysts for hydrogenations†
Abstract
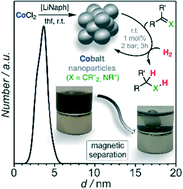
The search for new hydrogenation catalysts that replace noble metals is largely driven by sustainability concerns and the distinct mechanistic features of 3d transition metals. Several combinations of cobalt precursors and specific ligands in the presence of reductants or under high-thermal conditions were reported to provide active hydrogenation catalysts. This study reports a new method of preparation of small, monodisperse Co(0) nanoparticles (3–4 nm) from the reduction of commercial CoCl2 in the absence of ligands or surfactants. High catalytic activity was observed in hydrogenations of alkenes, alkynes, imines, and heteroarenes (2–20 bar H2). The magnetic properties enabled catalyst separation and multiple recyclings.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...