An ion exchange approach assembled multi-dimensional hierarchical Fe–TiO2 composite micro-/nano multi-shell hollow spheres for bacteria lysis through utilizing visible light†
Abstract
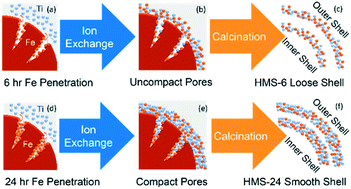
The ion exchange approach demonstrates the fabrication of the hierarchical, multi-shell, micro-/nano, Fe–TiO2 composite hollow spheres (HMS). The synthesis mechanism elucidates a novel technique to achieve a Fe–TiO2 composite multi-shell structure by first allowing Fe ions to penetrate the pores of carbonaceous spheres at room temperature. This is followed by ion exchange in a solvothermal treatment. Lastly, the outward diffusion of the Fe ions allows the inward diffusion of Ti ions to fill the voids created within the pores of the carbonaceous spheres and simultaneously form hierarchical thorns. The ion exchange enabled a deeper penetration of Ti ions into the pores of the carbonaceous spheres. The oxidization of the carbonaceous spheres leads to the convergence of deeply penetrated Ti–Fe ions which crystallize to form Fe–TiO2 composite multi-shell spheres. The HMS spheres revealed an agglomeration of 20 nm nanoparticulates and a uniform dispersion of Fe–TiO2 composite. Increasing the Fe ion penetration duration from 6 h up to 48 h was found to gradually reduce the band gap from 3.1 eV to approximately 2.7 eV. The synthesis mechanism elucidates the compaction of metal ions within the pores of the carbonaceous spheres which leads to a smoother inner sphere morphology and, consequently, the reduction in the mesopores diameter from 15 nm to 4 nm. The HMS demonstrate an enhanced physical lysis of 40% bacteria under dark conditions owing to the hierarchical thorn-like structure and an enhanced bactericidal capability to 70% under the irradiation of visible light over a period of 1 h. The initial physical lysis by the hierarchical thorn surface to the cell and the subsequent release of reactive oxygen species to degrade the ruptured bacteria wall or access the RNA/DNA led to further cell death.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...