Zirconia catalysed acetic acid ketonisation for pre-treatment of biomass fast pyrolysis vapours†
Abstract
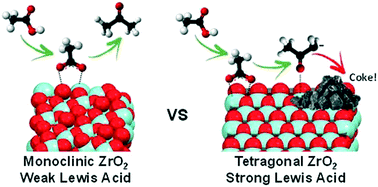
Crude pyrolysis bio-oil contains significant quantities of carboxylic acids which limit its utility as a biofuel. Vapour phase ketonisation of organic acids contained within biomass fast-pyrolysis vapours offers a potential pre-treatment to improve the stability and energy content of resulting bio-oils formed upon condensation. Zirconia is a promising catalyst for such reactions, however little is known regarding the impact of thermal processing on the physicochemical properties of zirconia in the context of it's corresponding reactivity for the vapour phase ketonisation of acetic acid. Here we show that calcination progressively transforms amorphous Zr(OH)4 into small tetragonal ZrO2 crystallites at 400 °C, and subsequently larger monoclinic crystallites >600 °C. These phase transitions are accompanied by an increase in the density of Lewis acid sites, and concomitant decrease in their acid strength, attributed to surface dehydroxylation and anion vacancy formation. Weak Lewis acid sites (and/or resulting acid–base pairs) are identified as the active species responsible for acetic acid ketonisation to acetone at 350 °C and 400 °C, with stronger Lewis acid sites favouring competing unselective reactions and carbon laydown. Acetone selectivity is independent of acid strength.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...