Potassium associated manganese vacancy in birnessite-type manganese dioxide for airborne formaldehyde oxidation†
Abstract
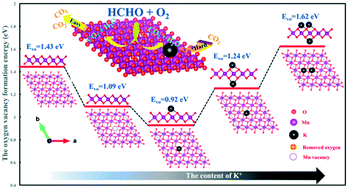
As a strategy for regulating the electronic structure of metal oxides, defect engineering has been widely studied, and the concentrations and spatial distributions of metal vacancies in metal oxides have always resulted in unprecedented properties. Moreover, alkali metals exhibit a universal promotion effect on catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde (HCHO). Herein, a kind of birnessite-type manganese dioxide (MnO2) with many Mn vacancies was hydrothermally synthesized for catalytic oxidation of HCHO. The significant effect of the K+ content on the structure, morphology and catalytic activity of birnessite-type MnO2 for HCHO oxidation was systematically studied for the first time. Initially, the increasing content of K+ obviously improved the catalytic performance for HCHO oxidation due to the considerable enhancement of the lattice oxygen activity. However, due to interaction with the excess K atoms, the oxygen atoms nearest to the K atoms were more stable and their mobility decreased, which was confirmed by experimental characterization and DFT (density functional theory) calculation. Moreover, the excess K+ increased the amount of surface basic sites, making CO2 difficult to desorb. Thus, there was an optimal K+ content to promote the activity of birnessite-type MnO2. With moderate K+ content in the birnessite-type MnO2, excellent catalytic activity for HCHO oxidation was achieved (T50% = 56 °C; T90% = 82 °C) under 100 ppm of HCHO and ∼90 L gcat−1 h−1 of gas hourly space velocity (GHSV). The present work provided an insight into the structure–activity relationship between birnessite-type MnO2 and its catalytic activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...