The stabilization mechanism and size effect of nonpolar-to-polar crystallography facet tailored ZnO nano/micro rods via a top-down strategy†
Abstract
A simple and efficient top-down strategy, the chemical vapor etching method, is reported for synthesizing corrugated ZnO nano/micro rods (NRs). The stabilization mechanism of this unique nanostructure has been determined through a combination of aberration-corrected field emission scanning electron microscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and first-principles calculations. The experimental data are in good agreement with the theoretical calculations, and a remarkable nonpolar-to-polar surface faceting transition is demonstrated. The corrugated-shaped structure results from the remarkable stability of the defect-induced reconstructions (O vacancy, Zn–Zn dimer), which makes the high-index polar {30![[3 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0033_0304.gif) 1} and {10
1} and {10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif)
![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) } planes lower in energy compared to the nonpolar {10
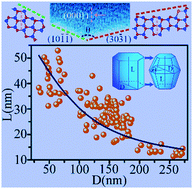
} planes lower in energy compared to the nonpolar {10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0} plane. Based on the results of first-principles surface calculations, a general formula is established to provide an accurate description of the unusual size effect of the length of the corrugated unit vs. the NR diameter, and it also offers direct explanations for certain experimental observations. The present study deepens our atomic-level understanding of the detailed structure and stability of polar surface decorated corrugated ZnO NRs, and points to a viable path towards designing polar-stable wurtzite structures.
0} plane. Based on the results of first-principles surface calculations, a general formula is established to provide an accurate description of the unusual size effect of the length of the corrugated unit vs. the NR diameter, and it also offers direct explanations for certain experimental observations. The present study deepens our atomic-level understanding of the detailed structure and stability of polar surface decorated corrugated ZnO NRs, and points to a viable path towards designing polar-stable wurtzite structures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...