How changes in interfacial pH lead to new voltammetric features: the case of the electrochemical oxidation of hydrazine†
Abstract
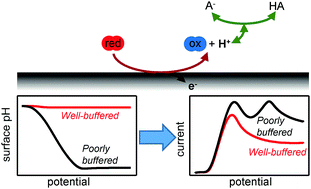
The electrochemical oxidation of hydrazine was investigated in strongly and weakly pH buffered solutions to reveal the role of buffer capacity in proton–electron transfer redox reactions. In sufficiently buffered solutions, a single voltammetric feature was observed. However, increasing the hydrazine concentration (or, equivalently, moving to an insufficiently buffered solution) gave rise to a second voltammetric feature. These results are rationalised with a conceptually simple model and finite element simulations. We demonstrate that the new voltammetric feature is caused by a large change in the pH at the electrode surface as the reaction proceeds. Importantly, we show that the occurrence of additional voltammetric features are general for proton–electron transfer reactions in insufficiently buffered solutions, and should not be confused with changes in the reaction mechanism.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...