Spectrum of hydrodynamic volumes and sizes of macromolecules of linear polyelectrolytes versus their charge density in salt-free aqueous solutions†
Abstract
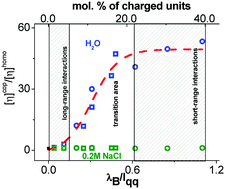
Molecular characteristics of statistical copolymers based on hydrophilic poly(N-methyl-N-vinylacetamide) have been monitored throughout the entire possible range of charge density from 1.5 to 39 mol%. Different trends in the dependence of intrinsic viscosity on the average charge density of polymer chains at minimal ionic strength were revealed. A new parameter, lqq/Abare, describing this behavior was proposed (lqq is the average distance between the neighboring charges along the chain, and Abare is the statistical segment length of a non-charged homologue). For polyelectrolyte chains, this parameter allows the regions of charge density values where electrostatic long-range or short-range interactions dominate to be indicated. Two homologous series of copolymers were characterized by methods of molecular hydrodynamics under conditions of suppressed charge effects. Intrinsic viscosity in salt-free solutions characterizing an individual macromolecule was estimated by a method proposed earlier [Pavlov et al., Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2006, 79, 1407–1412].


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...