Atomic-scale study of the formation of sodium–water complexes on Cu(110)
Abstract
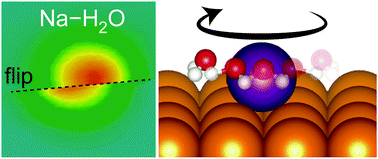
We observed individual sodium (Na) atoms and their complexes with water molecules on Cu(110) with scanning tunneling microscopy at 6 K. We induced the reaction of a Na adatom with one or two water molecules, which yielded two kinds of Na–water complexes. Density functional theory calculations were performed to study the structure of the complexes, which revealed that the water molecules are bonded to a Na atom along the [1![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0] direction via an oxygen atom with the hydrogen atoms pointing toward the Cu atoms of the surface. The 1 : 1 Na–water complex is stablized by 225 meV upon bond formation, and the ligand water moves back and forth around the Na atom. The complex can accommodate another water molecule to yield a 1 : 2 Na–water complex with an energy gain of 214 meV. The atomic-scale identification of the alkali–water complexes would give fundamental insights into the hydration process of alkali cations and their specific adsorption onto metal electrodes.
0] direction via an oxygen atom with the hydrogen atoms pointing toward the Cu atoms of the surface. The 1 : 1 Na–water complex is stablized by 225 meV upon bond formation, and the ligand water moves back and forth around the Na atom. The complex can accommodate another water molecule to yield a 1 : 2 Na–water complex with an energy gain of 214 meV. The atomic-scale identification of the alkali–water complexes would give fundamental insights into the hydration process of alkali cations and their specific adsorption onto metal electrodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...