Average orientation of a fluoroaromatic molecule in lipid bilayers from DFT-informed NMR measurements of 1H–19F dipolar couplings†
Abstract
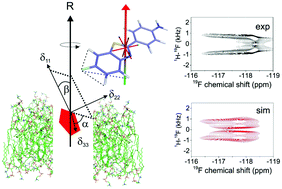
Fluorine is often incorporated into the aromatic moieties of synthetic bioactive molecules such as pharmaceuticals and disease diagnostics in order to alter their physicochemical properties. Fluorine substitution may increase a molecule's lipophilicity, thereby enabling its diffusion across cell membranes to enhance bioavailability or to exert a direct physiological effect from within the lipid bilayer. Understanding the structure, dynamics and orientation of fluoroaromatic molecules in lipid bilayers can provide useful insight into the effect of fluorine on their mode of action, and their interactions with membrane-embedded targets or efflux proteins. Here we demonstrate that NMR measurements of 19F chemical shift anisotropy combined with 1H–19F dipolar coupling measurements together report on the average orientation of a lipophilic fluoroaromatic molecule, 4-(6-fluorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)aniline (FBTA), rapidly rotating within a lipid bilayer. The 19F chemical shift tensor orientation in the molecular frame was calculated by density functional theory and corroborated by 1H–19F PISEMA NMR. It was then possible to analyse the line shapes of proton-coupled and proton-decoupled 19F spectra of FBTA in chain perdeuterated dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC-d54) bilayers to restrict the average axis of molecular reorientation of FBTA in the bilayer to a limited range orientations. This approach, which exploits the high sensitivity and gyromagnetic ratios of 19F and 1H, will be useful for comparing the membrane properties of related bioactive fluoroaromatic compounds.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...