Electro-wetting of a nanoscale water droplet on a polar solid surface in electric fields†
Abstract
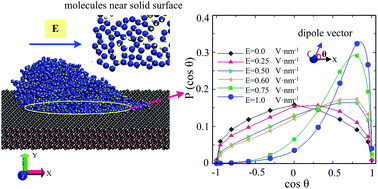
Molecular dynamics simulations were applied to study the wetting properties of nanoscale droplets on a polar silica solid substrate subjected to constant and alternative electric fields with various field frequencies. Results show that the external applied electric fields have significant effects on the wetting of the nanoscale droplet on a polar solid substrate. The droplet spreads asymmetrically under the effect of the external applied field, and this asymmetry culminates to the maximum when the electric field equals to 0.45 V nm−1. For an electric field of 1.0 V nm−1, the dynamic electro-wetting process undergoes two stages even with a symmetric equilibrium spreading state. The stage A–B transition happens suddenly when molecules on the leading edge drop onto the solid surface due to the strong attraction of the solid substrate. Furthermore, under the alternative electric field with a different GHz frequency range, it was observed that the spreading asymmetry was weakened by increasing the field frequency and the nanoscale water droplet shape changes very slightly above a threshold frequency. Accompanied by the shape variation of water droplets, the molecular dipole orientations of water molecules experience a remarkable change from a random disordered distribution to an ordered profile because of the realignment of water molecules induced by electric fields. In addition, the polar solid surface has significant effects on the rearrangement of water molecules compared with a single droplet. Thus, the electro-wetting behaviors of water droplets on a silica solid surface are determined by the competing intermolecular forces among water, solid and the electric field.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...