The effect of KH on enhancing the dehydrogenation properties of the Li–N–H system and its catalytic mechanism†
Abstract
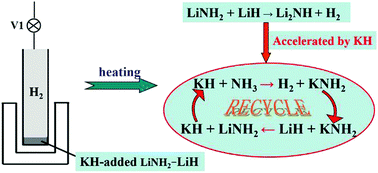
Although recent works demonstrated that some potassium compounds that can be converted to KH during ball-milling or heat-treatment have obvious effects on enhancing the dehydrogenation properties of the Li–N–H system, the effect of KH on enhancing the dehydrogenation properties of the Li–N–H system and its catalytic mechanism remain unclear. In this study, the hydrogen desorption properties of the LiNH2–LiH system with alkali metal hydrides (LiH, NaH, or KH) were investigated and discussed. We find that the three types of hydrides are effective for enhancing the hydrogen desorption properties of the LiNH2–LiH system, among which, KH shows the best effect. In comparison with the broad shaped hydrogen desorption curve of the LiNH2–LiH composite without additive, the hydrogen desorption curve of the LiNH2–LiH–0.05KH composite becomes narrow. The dehydrogenation onset temperature of the LiNH2–LiH–0.05KH composite is decreased by approximately 20 °C, and the dehydrogenation peak temperature is lowered by approximately 30 °C. Moreover, the reversibility of the LiNH2–LiH system is enhanced drastically by the addition of KH. On the basis of previous reports and present experimental results, the mechanism for the enhancement of the dehydrogenation properties in the KH-added Li–N–H system is proposed. The reason for the improvement of the hydrogen desorption kinetics is that KH has superior reactivity with NH3 and plays the role of a catalyst to accelerate hydrogen release by cyclic reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...