Different photoisomerization routes found in the structural isomers of hydroxy methylcinnamate†
Abstract
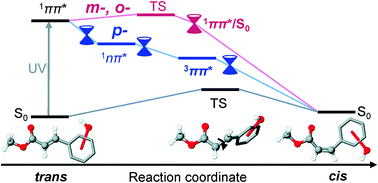
An experimental and theoretical study has been carried out to elucidate the nonradiative decay (NRD) and trans(E) → cis(Z) isomerization from the S1 (1ππ*) state of structural isomers of hydroxy methylcinnamate (HMC); ortho-, meta- and para-HMC (o-, m- and p-HMC). A low temperature matrix-isolation Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study revealed that all the HMCs are cis-isomerized upon UV irradiation. A variety of laser spectroscopic methods have been utilized for jet-cooled gas phase molecules to investigate the vibronic structure and lifetimes of the S1 state, and to detect the transient state appearing in the NRD process. In p-HMC, the zero-point level of the S1 state decays as quickly as 9 ps. A transient electronic state reported by Tan et al. (Faraday Discuss. 2013, 163, 321–340) was reinvestigated by nanosecond UV-tunable deep UV pump–probe spectroscopy and was assigned to the T1 state. For m- and o-HMC, the lifetime at the zero-point energy level of S1 is 10 ns and 6 ns, respectively, but it becomes substantially shorter at an excess energy higher than 1000 cm−1 and 600 cm−1, respectively, indicating the onset of NRD. Different from p-HMC, no transient state (T1) was observed in m- nor o-HMC. These experimental results are interpreted with the aid of TDDFT calculations by considering the excited-state reaction pathways and the radiative/nonradiative rate constants. It is concluded that in p-HMC, the trans → cis isomerization proceeds via a [trans-S1 → 1nπ* → T1 → cis-S0] scheme. On the other hand, in o- and m-HMC, the isomerization proceeds via a [trans-S1 → twisting along the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C double bond by 90° on S1 → cis-S0] scheme. The calculated barrier height along the twisting coordinate agrees well with the observed onset of the NRD channel for both o- and m-HMC.
C double bond by 90° on S1 → cis-S0] scheme. The calculated barrier height along the twisting coordinate agrees well with the observed onset of the NRD channel for both o- and m-HMC.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...