Solvation of diclofenac in water from atomistic molecular dynamics simulations – interplay between solute–solute and solute–solvent interactions†
Abstract
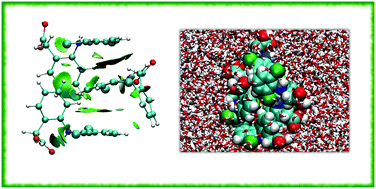
The solubility–permeability relationship of active pharmaceutical ingredients determines the efficacy of their usage. Diclofenac (DCL), which is a widely used nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, is characterized by extremely good membrane permeability, but low water solubility limiting drug effectiveness. The present research focuses on the fundamental explanation of this limitation using the combination of ab initio and classical molecular dynamics simulations of different ionic forms of DCL in water, namely, ionized, un-ionized and the mixture of them both. The analysis of diclofenac solvation in an aqueous environment is used to understand the origin of drug precipitation, especially in gastric pH. The used computational approach reveals the formation of micelle-like self-associated aggregates of diclofenac in water as the result of intermolecular π–π interactions and C–H⋯π hydrogen bonds. The DCL aggregation in water is shown to depend mostly on drug concentration, protonation and temperature of the aqueous environment. The detected self-association properties of the drug in water are likely to be of great importance during the development of new drug formulations and fabrication of drug adsorbents for wastewater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...