Local structure and hydrogen bond characteristics of imidazole molecules for proton conduction in acid and base proton-conducting composite materials†
Abstract
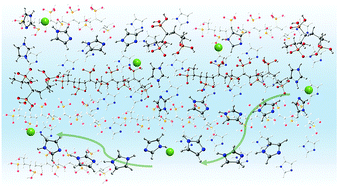
Composite materials of acidic polymers and basic molecules have high proton-conductivity. Understanding the proton conduction mechanism of the composite materials, which depends on hydrogen bond characteristics, is an important task for developing materials with high proton-conductivity. This work is focused on poly(vinylphosphonic acid)–imidazole and alginic acid–imidazole as examples of composite materials of acidic polymers and basic molecules and examines the local structure and hydrogen bond characteristics of imidazole (Im) molecules in composite materials using density functional theory. The results show that Im molecules interact strongly with polymeric acids in these composite materials and that the interaction energy increases with the increase in the number of Im molecules. The rotational motion of Im molecules occurs in the segment where only Im molecules without excess protons are hydrogen-bonded to each other. The calculation results for the various segments, which depend on the hydrogen bonding environment, show that the proton conduction process in composite materials consists of the following steps: proton transfer in the segment where Im molecules interact with polymeric acids, proton transfer in the segment where Im molecules are affected by excess protons, and Grotthuss diffusion with reorientation of Im molecules in the segment where only Im molecules without excess protons are bonded to each other.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...