Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/poly(3-methylthiophene) core–shell nanocomposites with improved structural and electronic properties of the conducting polymer component†
Abstract
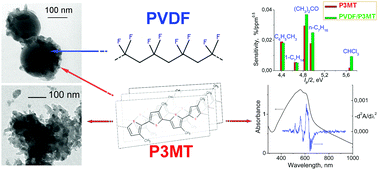
We report significant improvements in the structure and electronic properties of a poly(3-alkylthiophene) representative, namely poly(3-methylthiophene) (P3MT), when it is synthesized in the presence of submicron electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) particles. The applied template oxidative synthesis leads to the formation of the PVDF/P3MT composite consisting of core–shell particles. The shells are constituted with a monolayer of 20–40 nm nanoparticles of the doped P3MT (P3MT-Cl) precipitated at the surface of the spherical PVDF cores. This morphology differs strongly from the hierarchical one of the neat P3MT synthesized without PVDF particles. In the latter case, 20–60 nm P3MT nanoparticles form ∼200 nm aggregates, which, in turn, are arranged in a few micrometer agglomerates. Furthermore, we demonstrate that compared to the neat polymer, doped P3MT in the shells of the composite is characterized with higher effective conjugation length, regioregularity of the molecular structure, improved intrachain packing order and lower bipolaron/polaron ratio. These features of the PVDF/P3MT composite strongly suggest applicability of this material in various electronic devices. As a proof of concept, we report on an improved sensing performance of the PVDF/P3MT-Cl composite compared with the neat P3MT-Cl in detection of several volatile organic compounds known as markers for some diseases and toxic substances. We have discovered that the maximal improvement in the sensor response magnitude corresponds to the case when the values of the analyte electronegativity and polythiophene work function are close. We associate this behavior with a higher surface dipole component of the work function of the PVDF/P3MT-Cl composite compared to that of the neat conducting polymer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...