Energy transfer and charge separation dynamics in photoexcited pyrene–bodipy molecular dyads†
Abstract
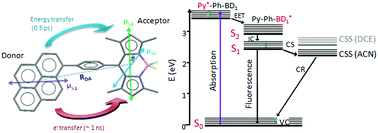
The photophysical properties of two pyrene–bodipy molecular dyads, composed of a phenyl-pyrene (Py-Ph) linked to the meso position of a bodipy (BD) molecule with either H-atoms (BD1) or ethyl groups (BD2) at the 2,6 positions, are investigated by stationary, nanosecond and femtosecond spectroscopy. The properties of these dyads (Py-Ph-BD1 and Py-Ph-BD2) are compared to those of their constituent chromophores in two solvents namely 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE) and acetonitrile (ACN). Stationary spectroscopy reveals a weak coupling among the subunits in both dyads. Excitation of the pyrene (Py) subunit leads to emission that is totally governed by the BD subunits in both dyads pointing to excitation energy transfer (EET) from the Py to BD chromophore. Femtosecond fluorescence and transient absorption spectroscopy reveal that EET takes place within 0.3–0.5 ps and is mostly independent of the solvent and the type of the BD subunit. The EET lifetime is in reasonable agreement with that predicted by Förster theory. After EET has taken place, Py-Ph-BD1 in DCE and Py-Ph-BD2 in both solvents decay mainly radiatively to the ground state with 3.5–5.0 ns lifetimes which are similar to those of the individual BD chromophores. However, the excited state of Py-Ph-BD1 in ACN is quenched having a lifetime of 1 ns. This points to the opening of an additional non-radiative channel of the excited state of Py-Ph-BD1 in this solvent, most probably charge separation (CS). Target analysis of the TA spectra has shown that the CS follows inverted kinetics and is substantially slower than the recombination of the charge-separated state. Occurrence of CS with Py-Ph-BD1 in ACN is also supported by energetic considerations. The above results indicate that only a small change in the structure of the BD units incorporated in the dyads significantly affects the excited state dynamics leading either to a dyad with long lifetime and high fluorescence quantum yield or to a dyad with ability to undergo CS.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...