Influence of macroscopic defects on the corrosion behavior of U–0.79 wt%Ti alloy in sodium chloride solution†
Abstract
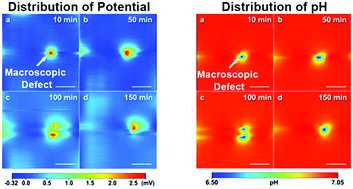
Uranium alloys containing a low concentration of titanium have received wide attention due to their greatly enhanced corrosion resistance and outstanding mechanical performances. Herein, we investigated the effect of macroscopic defects on the corrosion behavior of U–0.79 wt%Ti (denoted as U–Ti) alloy in 0.01 M NaCl solution using traditional electrochemical testing technologies and a novel scanning electrochemical composite probe (SECP). The results demonstrate that pitting corrosion occurs rapidly on the alloy surface due to macroscopic defects. Moreover, macroscopic defects led to a decrease in corrosion potential and polarization resistance, and an increase in corrosion current density. Furthermore, the potential and pH value distributions were detected in the same region using the composite probe. The results show that the region around the macroscopic defects become corrosion-active positions and the potential difference (vs. the average potential of the alloy surface) in this area is significantly higher than that at positions without macroscopic defects, while the opposite was observed for the pH value distribution. In addition, the distribution of the vertical direction (Z) potential at the active point was clearly different from that at the inactive point. A possible reason for this could lie in the difference in the electric field distribution and electrode reaction type between the active point and inactive point on the alloy surface.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...