Investigation of V2O5 as a low-cost rechargeable aqueous zinc ion battery cathode
Abstract
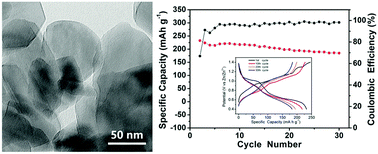
Rechargeable aqueous zinc ion batteries (ZIBs) are highly desirable for large-scale energy storage due to their advantages of safety and low-cost. Development of advanced cathodes for use in aqueous ZIBs is urgently needed. Herein, we report a low-cost rechargeable aqueous Zn–V2O5 cell with 3 M ZnSO4 electrolyte that demonstrates high zinc storage capability. We also investigated the effect of different types/concentrations of the aqueous electrolytes on the performance of the Zn–V2O5 cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...