Evolution of 2D tin oxides on the surface of molten tin†
Abstract
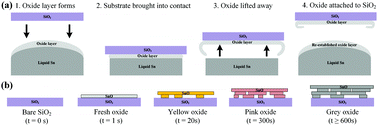
The exfoliation of two dimensional (2D) oxides, established on the surface of specific liquid metals, has recently been introduced. One such liquid metal is molten tin, which forms a variety of surface 2D oxides. However, the development behaviour of these surface tin oxides is still unknown. Here the evolution of stoichiometry and thickness from single-layer SnO to highly oxidised multi-layer SnO2 in ambient oxygen is explored.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...