TPAOH assisted size-tunable Gd2O3@mSi core–shell nanostructures for multifunctional biomedical applications†
Abstract
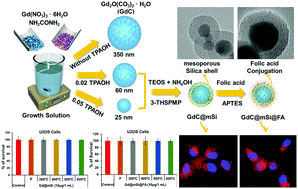
We report a facile and large-scale synthesis of size-tunable and nontoxic mesoporous silica-coated Gd2O3:Eu3+ (Gd@mSi) core–shell nanostructures using a TPAOH assisted modified UHP technique. The role of TPAOH in controlling the particle size was evaluated. The potentiality of these Gd@mSi core–shell nanoparticles before and after folic acid conjugation was established by in vitro fluorescence microscopy of the U2OS cell lines for cancer imaging and therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...