Glutathione-induced amino-activatable micellar photosensitization platform for synergistic redox modulation and photodynamic therapy†
Abstract
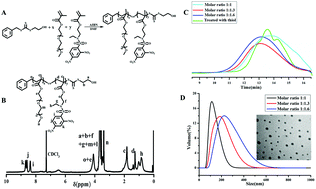
In recent years, photodynamic therapy (PDT) was considered to be a promising cancer treatment modality, however, the therapeutic efficiency was often attenuated by the intrinsic antioxidant defense systems. Herein, a kind of novel glutathione-induced amino-activatable micelle was designed, which was expected to weaken the antioxidant capacity and in the meantime release the photosensitizer by the exhaustion of intracellular glutathione (GSH). The amphiphilic poly(ethylene glycol)-(2-((2,4-dinitro-N-(ethyl) phenyl)sulfonamido) ethyl methacrylate) copolymers were synthesized and assembled into a core–shell nano structure in aqueous media. The nano structure demonstrated high sensitivity and selectivity to bio-thiols in vitro and in vivo. Subsequently, pheophorbide a (PhA) was encapsulated as the model photosensitizer. Upon internalization by HepG2 cells, the strongly electron-withdrawing 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl groups on the PADEE segments were readily cleaved by GSH, during which time the secondary amino groups (pKb = 11.32) were recovered and completely protonated, leading to disassembly of the micelles and rapid release of PhA. Importantly, the consumption of GSH weakened the intracellular antioxidant capacity, resulting in the synergetic accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) under laser irradiation. As a result, this micellar photosensitization system could overcome the antioxidant capacity of advanced stage tumors through a simultaneous extrinsic and intrinsic strategy, facilitating therapeutic efficiency. These results demonstrate that the as-designed micelles provide a versatile photosensitization platform for on-demand PDT.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...