Analyzing the antiseptic capacity of silver-functionalized poly(ethylene glycol)–heparin hydrogels after human whole blood exposure†
Abstract
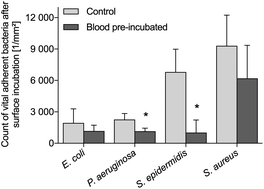
Advanced blood contacting biomaterials are designed to combine antiseptic and anticoagulant functionalities. Here, we present a new in vitro methodology for the analysis of bacterial adhesion and growth after the preceding human whole blood incubation of the tested materials. Poly(styrene) surfaces as well as thrombin-responsive and non-responsive poly(ethylene glycol)–heparin hydrogel coatings, with and without silver functionalization, were analyzed with this approach using freshly drawn human whole blood and various human pathogens (Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli). Adsorbed blood proteins and adherent immune cells were observed to suppress bacterial colonization on poly(styrene) surfaces. Silver functionalization of responsive and non-responsive poly(ethylene glycol)–heparin hydrogels had no influence on microbial attachment but decreased bacterial proliferation and viability. Whole blood pre-incubation did not affect the antimicrobial properties of the tested silver-modified hydrogels. In sum, our introduced multistage incubation test revealed the antibacterial effects as well as antiseptic-permissive characteristics of blood-borne interfacial layers on polymeric biomaterials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...