A label-free ultrasensitive and selective strategy for Pb(ii) assay by a multifunctional DNA probe-mediated rolling-circle amplified synthesis of the G-quadruplexes†
Abstract
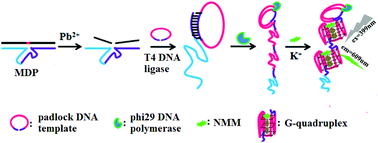
We report a label-free ultrasensitive and selective strategy for Pb(II) assay by a multifunctional DNA probe (MDP)-mediated rolling-circle amplified synthesis of the G-quadruplexes. The MDP acted as a target recognition probe, a catalytic DNAzyme and a primer of rolling-circle amplification (RCA). The presence of Pb(II) can induce the conformational switching of the MDP, resulting in the cleavage of the S-DNA in the MDP to release an E-DNA. The released E-DNA then initiated a RCA reaction with a reasonably devised padlock DNA template to produce an accumulated amount of repeated sequences. The RCA product in the present work was designed as a G-rich sequence, which could fold into thousands of G-quadruplex units. The G-quadruplex formed by RCA can specifically bind to NMM to result in an amplified fluorescence signal. Through these cascade amplifications, Pb(II) ions can be detected at as low as 94.29 pM, which is much lower than those reported in related literature. We expect that this amplification strategy might be helpful in the design of a highly sensitive analytical platform for wide application in environmental and biomedical fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...