Inkjet printing Ag nanoparticles for SERS hot spots†
Abstract
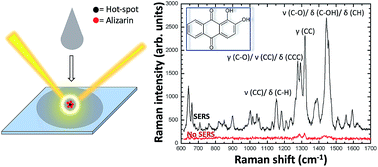
A novel inkjet printing based approach is developed for the fabrication of a customizable platform on glass substrates allowing for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) detection of analytes up to single hot spots generated by the spontaneous aggregation of Ag nanoparticles (Ag NPs) in pL scale droplets. After drying the printed droplets under ambient conditions, trace amounts of the analyte can be detected by SERS given the proximity to NP hot spots. By employing alizarin (10−5 M) as a model system and scaling the ink droplet volume from 1 nL to 10 pL, the absolute quantity of hot spots has been derived in the printed droplets allowing detecting up to a few molecules in proximity to individual hot spots. Besides requiring a small amount of analyte (around 0.1 femtomoles) and colloidal Ag (≈20 attograms) per droplet, we show the possibility to obtain a very accurate determination of the enhancement factor (>104).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...