Dual-quenching strategy for determination of ATP based on aptamer and exonuclease I-assisted electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer
Abstract
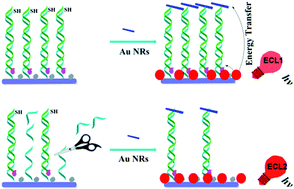
We report a dual-quenching strategy for highly sensitive detection of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) using electrochemiluminescence (ECL) recovery based on the exonuclease-assisted reduction in amounts of both ferrocene and ECL-RET acceptor (Au nanorod). Ru(bpy)32+ was used as the ECL donor due to its high quantum yield and high ECL intensity. First, ATP aptamer labeled with ferrocene (Fc) was introduced onto the electrode surface through the hybridization of the aptamer with capture DNA. Moreover, the 3′ terminus of the capture DNA had been designed to be modified with a thiol group. In the absence of ATP, the capture DNA could not be digested by exonuclease I (Exo I), resulting in a decreased background ECL signal. Additionally, a large amount of Au nanorods was conjugated at the 3′-terminus of capture DNA through Au–S bonds, leading to further reduction of the background ECL signal due to the ECL resonance energy transfer (ECL-RET) between Ru(bpy)32+ and Au nanorods. However, in the presence of ATP, the ECL signal could be enhanced significantly not only because of the liberation of the Fc-aptamer from the electrode surface, but also due to the reduced concentration of Au nanorods after the cleavage of single-stranded capture DNA in the 3′ to 5′ direction with Exo I. This method provides a simple and sensitive approach for ATP detection and holds great potential in cancer-biomarker assays.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...