A novel high hydrothermal stability amino-functionalized stationary phase prepared by a vapour deposition method
Abstract
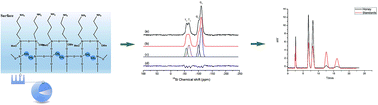
A novel bistrimethoxysilylethane hydrolysis aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (BTME-H-APS) silica stationary phase was prepared through a three-step vapour deposition method. Compared to the toluene bonding method, the vapour deposition route has the benefits of lower organic solvent consumption and easy process controlling. The structure of the hybrid modified silica substrate was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and solid-state 13C CP/MAS NMR. Following elemental analysis, the surface density of the amine group was calculated at 3.44 μmol m−2, which is similar to the value of the commercial amine phase. The BTME-H-APS stationary phase exhibited a higher hydrothermal stability and longer service life at high alkaline conditions, due to the relative higher carbon loading and cross-linking degree of the BTME-H-APS phase, which was confirmed by the solid-state 29Si NMR analysis. Then, the chromatographic evaluation demonstrated an equal, or even higher, separation ability in mixed-mode hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)/reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RPLC), normal-phase liquid chromatography (NPLC) and ion-exchange chromatography (IEC) models on BTME-H-APS compared with a conventional amine column. The BTME-H-APS phase was successfully applied to the separation of carbohydrates in honey for authenticity identification. This bistrimethoxysilylethane hybrid organosilane method reported here can be further applied in the preparation of other stationary phases with increased hydrothermal stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...