The study of bismuth ions in drinking water at ultratrace levels by a microwave plasma torch coupled with linear ion trap mass spectrometry
Abstract
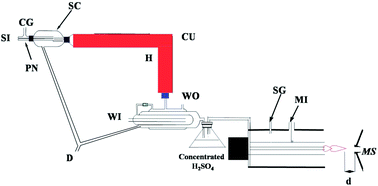
A microwave plasma torch (MPT) can be used as a simple and low power-consumption ambient ion source and coupled with several kinds of mass spectrometers. When MPT mass spectrometry is applied for the detection of some metal elements, the metallic ions exhibit some novel features that are significantly different from those obtained by the traditional ICP mass spectrometry and may be helpful for the detection of metal elements in water. As a representative metal element of group VA, bismuth is of crucial importance, which is widely applied in modern industry, and has great potential impact on human health. Herein, we presented a novel study on the complex ions of bismuth in water using an MPT ion source coupled with a linear ion trap mass spectrometer (LTQ-MS). These complex ions were produced by the interaction of a plasma flame with wet aerosols first introduced through the central tube of the MPT torch and then into the inlet of the mass spectrometer; we also used another quadrupole mass spectrometer (QMS) for the comparison of different ionic patterns obtained from these two mass spectrometers. Moreover, the feature fragment patterns of these ions have been explained via a multi-step collision-induced dissociation process. Under the optimized conditions and negative working mode of LTQ-MS, the limit of detection (LOD) of bismuth in the LTQ-MS MS2 procedure was 0.028 μg L−1, which reached ultratrace levels. The linear range covers the interval of 0.5–50 μg L−1, and the relative standard deviation (RSD, n = 6) alters between 1.7% and 7.0%. The standard addition recovery rates of five brands of drinking water were between 83.74% and 113.70%. These results demonstrate that the MPT MS is a promising and hopeful tool to detect metallic ions in water, which can also be applied in many other fields such as in environmental controlling, hydrogeology, water quality inspection, and food analysis. In addition, MPT MS could be used as a supplement of ICP-MS for the rapid and on-site analysis of metal ions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...