Microfluidic-based measurement of RBC aggregation and the ESR using a driving syringe system†
Abstract
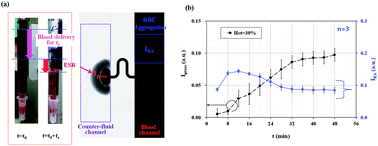
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and red blood cell (RBC) aggregation have been widely used to detect inflammatory diseases. In this study, a simple measurement method is proposed to simultaneously quantify RBC aggregation and the ESR in a driving syringe. A microfluidic device composed of inlets, outlets, and identical parallel channels (counter-fluid channel and blood channel) is developed. The counter-fluid channel and the blood channel are filled with a 40% glycerin solution and blood, respectively. To control counter-fluid flow, a pinch valve is installed at a specific position along the length of the tube connected to the counter-fluid channel. Blood in the driving syringe (Vblood = 0.7–1 mL, hematocrit = 30%) is delivered to the microfluidic device at a pulse-shaped flow rate (Q0 = 1 mL h−1, T = 240 s). As blood pressure is proportional to the volume of RBCs in the counter-fluid channel, blood pressure is measured as Ipress by quantifying the volume of RBCs in the counter-fluid channel. The ESR in the driving syringe is then measured as Ipress or the time constant of Ipress. RBC aggregation is evaluated as IRA by quantifying the image intensity of blood in the blood channel. Blood is first prepared by adding normal RBCs to a dextran solution (Cdextran = 0–10 mg mL−1). The ESR and RBC aggregation in the driving syringe significantly increase at higher dextran concentrations. Second, the proposed method is applied to detect heterogeneous blood samples that are prepared by mixing RBC-aggregated blood with RBC-hardened blood, partially (i.e., mixing ratio = 0, 0.5, and 1). Then, three different blood samples are completely separated with the two parameters (Ipress and IRA). In conclusion, the proposed method can be used to measure RBC aggregation and the ESR in a driving syringe by quantifying the blood pressure index and the RBC aggregation index.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...