Rapid and sensitive detection of viral nucleic acids using silicon microchips
Abstract
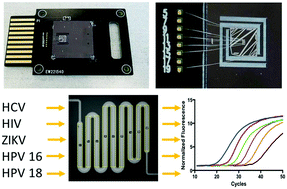
Clinical laboratory-based nucleic acid amplification tests (NAT) play an important role in diagnosing viral infections. However, laboratory infrastructure requirements and their failure to diagnose at the point-of-need (PON) limit their clinical utility in both resource-rich and -limited clinical settings. The development of fast and sensitive PON viral NAT may overcome these limitations. The scalability of silicon microchip manufacturing combined with advances in silicon microfluidics present an opportunity for development of rapid and sensitive PON NAT on silicon microchips. In the present study, we present rapid and sensitive NAT for a number of RNA and DNA viruses on the same silicon microchip platform. We first developed sensitive (4 copies per reaction) one-step RT-qPCR and qPCR assays detecting HCV, HIV, Zika, HPV 16, and HPV 18 on a benchtop real-time PCR instrument. A silicon microchip was designed with an etched 1.3 μL meandering microreactor, integrated aluminum heaters, thermal insulation trenches and microfluidic channels; this chip was used in all on-chip experiments. Melting curve analysis confirmed precise and localized heating of the microreactor. Following minimal optimization of reaction conditions, the bench-scale assays were successfully transferred to 1.3 μL silicon microreactors with reaction times of 25 min with no reduction in sensitivity, reproducibility, or reaction efficiencies. Taken together, these results demonstrate that rapid and sensitive detection of multiple viruses on the same silicon microchip platform is feasible. Further development of this technology, coupled with silicon microchip-based nucleic acid extraction solutions, could potentially shift viral nucleic acid detection and diagnosis from centralized clinical laboratories to the PON.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Coronavirus articles - free to access collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...