Multi-functional derivatization of amine, hydroxyl, and carboxylate groups for metabolomic investigations of human tissue by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry†
Abstract
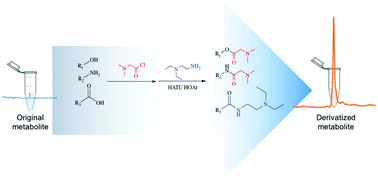
Metabolomics, the study of small molecules involved in cellular processes, offers the potential to reveal insights into the pathophysiology of disease states. Analysis of metabolites by electrospray mass spectrometry is complicated by their structural diversity. Amine, hydroxyl, and carboxylate groups all affect signal responses differently based on their polarity and proton affinity. This heterogeneity of signal response, sensitivity, and resistance to competing ionization complicates metabolite quantitation. Such limitations can be mitigated by a dual derivatization scheme. In this work, primary amine and hydroxyl groups are tagged with a linear acyl chloride head containing a tertiary amine tail, followed by carboxylate groups coupled to a linear amine tag with a tertiary amine tail. This tagging scheme increases analyte proton affinity and hydrophobicity. In the case of carboxylate groups, the inherent anionic charge is inverted to a cationic charge. This dual tagging is completed within 2.5 hours, diminishes adduct formation, and improves sensitivity by >75-fold. The average limit of detection for 23 metabolites was 38 nM and the R2 was 0.97. This process was used to investigate metabolite changes from human tissue. Examination of diabetic and non-diabetic human tissue showed marked changes in both energy metabolites and amino acids. Further examination of the tissue showed that HbA1C value is inversely correlated with fumarate levels. This technique potentially allows for the analysis of virtually all metabolites in a single analytical run. Thus, it may lead to a more complete picture of metabolic dysfunction in human disease.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...