Miniature diamond-anvil cells for FTIR-microspectroscopy of small quantities of biosamples†
Abstract
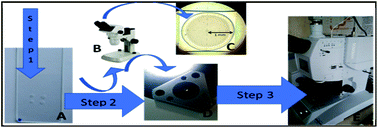
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy techniques and data analyses have become widely available, are easy to use, and are convenient for studies of various biosamples, especially in biomedical science. Yet, cultivation of cells and purification of cell components are costly, often methodically challenging, and time and labor consuming. Therefore, reduction of the sample amount is of high value. Here we propose a novel method for the analysis of small quantities of biosamples by FTIR-microscopy of dry films using a diamond-anvil cell (DAC). This approach allows us to decrease the sample volume at least a hundred times compared to that for a high-throughput screening device (HTS-XT, Bruker, Germany), while still obtaining homogeneous films, acquiring qualitative spectra, and using a conventional 15× objective instead of an ATR-objective. Both FTIR methods were applied for analyses of human colorectal cancer cell lines SW480 and SW620 cultured under hypoxic conditions to estimate the strengths and weaknesses of each approach. FTIR absorption spectra acquired by both methods were compared and no significant spectral differences were detected. It was shown that FTIR-microscopy of films on the DAC can be used for evaluation, screening, discrimination and identification of biochemical markers in biosamples like cells. We conclude that the DAC can be transferred to other biosamples like tissues, biofluids, their components and extracellular matrix, and is especially valuable when the available quantities of biosamples are limited.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...