Circulating levels of miR-122 increase post-mortem, particularly following lethal dosing with pentobarbital sodium: implications for pre-clinical liver injury studies
Abstract
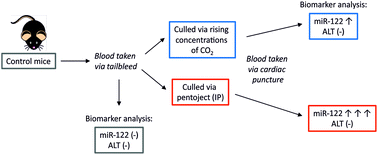
microRNA-122 (miR-122) is increasingly being measured in pre-clinical and clinical settings due to greater sensitivity and hepatic specificity compared to the gold standard liver injury biomarker alanine aminotransferase (ALT). In pre-clinical studies, various culling methods can be employed prior to collection of blood samples, including lethal injection with pentobarbital sodium (Pentoject). However, little is known about whether such an approach could alter the circulating levels of miR-122 and compromise the interpretation of data. We therefore exposed C57BL/6J mice to saline or the model hepatotoxin paracetamol and collected blood samples pre-cull (via tail bleed) and post-cull (via cardiac puncture following exposure to a rising concentration of CO2 or intraperitoneal injection of Pentoject). Compared to pre-cull levels there was a significant increase in serum miR-122 level in mice culled with CO2 and, to a much greater extent, in mice culled with Pentoject. As a result, whilst the serum level of miR-122 increased in Pentoject-culled animals exposed to paracetamol, the higher level in saline-treated mice rendered this difference statistically non-significant, in contrast to findings in animals culled with CO2. ALT levels were unaffected by sacrifice method. Consistent with the in vivo findings, exposure of primary mouse hepatocytes to Pentoject provoked a rapid and concentration-dependent release of miR-122 into the culture media. Thus, for optimal design and interpretation of data from pre-clinical liver injury studies in which miR-122 is to be used as a biomarker, we recommend that blood samples are collected pre-cull whenever possible, and that lethal injection with Pentoject is avoided.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...