MEMS analogous micro-patterning of thermotropic nematic liquid crystalline elastomer films using a fluorinated photoresist and a hard mask process†
Abstract
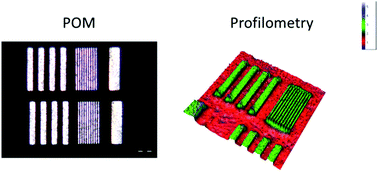
In this work, we present a method to pattern liquid crystal elastomers (LCEs) in the micrometer range without using any mechanical processing steps to prepare micron sized LCE actuators compatible with microelectromechanical system (MEMS) technology. Multi-layer spin-coating processes are developed to synthesise and structure 300–3500 nm thick LCE films. A water soluble sacrificial layer, a photoalignment layer and a LCE formulation, which is polymerised and crosslinked in its liquid crystal phase, are spin-coated successively onto a substrate. A fluorinated photoresist layer is used to structure LCE films with thicknesses up to 700 nm in a photolithographic and etching process. For thicker LCE films a hard mask process, using hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) as hard mask, is used. Film thicknesses and homogeneities are analysed with profilometry. Actuation motions of LCE layers are investigated before and after patterning and LCE patterns are investigated via (polarised optical) microscopy (POM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and profilometry. A resolution of 1.5–2.0 microns is achieved with the described techniques, which make deformable micron sized LCE actuators of variable shape and director orientation accessible. The presented results demonstrate the potential of LCEs in MEMS devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...