A flexible and self-formed sandwich structure strain sensor based on AgNW decorated electrospun fibrous mats with excellent sensing capability and good oxidation inhibition properties†
Abstract
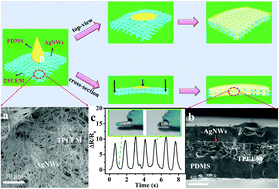
Strain sensors based on silver nanowires (AgNWs) have attracted a great deal of attention because of their diverse applications in electronic skin, smart textiles, and structural health monitoring, etc. However, the oxidation of silver nanowires has been bothering people and limits the use of these sensors. In this work, we report a high-performance strain sensor based on a composite of a thermoplastic polyurethane electrospun membrane (TPUEM) and polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) with a self-formed sandwich structure to address this problem. The strain sensor was fabricated via attaching the AgNWs onto the TPUEM by filtration to form a conductive network, followed by spin-coating using liquid PDMS. The sandwich structure was self-formed on the basis of the porosity of the TPU electrospun membrane and the liquidity of PDMS, providing effective protection of AgNWs from the air. As a result, the strain sensor exhibited excellent conductivity of 50 S cm−1 with almost no change in 30 days. The flexible AgNW-based sensor could detect both stretching and bending deformations with high sensitivity, excellent reliability and remarkable stability. Moreover, the developed strain sensor could be utilized to detect human motions such as finger bending, wrist movements and hand-clenching movements, indicating that it had huge potential in wearable electronics applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...