Altering polarization attributes in ferroelectric metallo-cavitands by varying hydrated alkali-metal guest cations†
Abstract
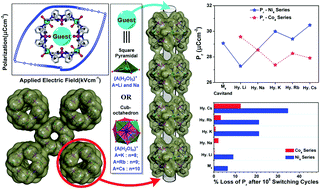
Supramolecular ferroelectrics have emerged as an exciting topic of research for both fundamental understanding and practical applications in the areas of energy and electronics. Here, we describe the synthesis of two metallo-cavitands [{M4L8(H2O)8}⊃9(H2O)]·(NO3)8·x(H2O) [M![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) Ni2+ (1) or Co2+ (2)] and demonstrate solid-state host–guest behavior and ferroelectricity in the presence of various hydrated alkali metal cations (Hy-A) in their intrinsic voids. Due to the confinement effects of the cavitands, the degree of hydration observed for these alkali metal ions is on the upper side; in particular, the K+, Rb+ and Cs+ ions show high hydration numbers of 8, 9 and 10, respectively. Ferroelectric studies on 1, [Hy-A]⊂1 and [Hy-A]⊂2 assemblies show remnant polarization (Pr) values ranging from 27 to 30 μC cm−2 with concomitant variations in the coercive field (Ec) values at a lower frequency of 0.1 Hz. The observed features for the P–E loop characteristics of all the assemblies are reminiscent of triglycine sulphate (TGS) and certain other supramolecular ferroelectrics. Interestingly, ferroelectric fatigue measurements on all these systems show sizable variations as the cavitands with hard Li+ ions exhibiting the maximum (fatigue) tolerance and the ones with higher polarizable Cs+ ions show a reduction in Pr values up to 35%, after 105 switching cycles. The results signify the effect of encapsulated guest molecules in altering the polarization attributes (Pr, Ec and fatigue tolerance) via host–guest interactions.
Ni2+ (1) or Co2+ (2)] and demonstrate solid-state host–guest behavior and ferroelectricity in the presence of various hydrated alkali metal cations (Hy-A) in their intrinsic voids. Due to the confinement effects of the cavitands, the degree of hydration observed for these alkali metal ions is on the upper side; in particular, the K+, Rb+ and Cs+ ions show high hydration numbers of 8, 9 and 10, respectively. Ferroelectric studies on 1, [Hy-A]⊂1 and [Hy-A]⊂2 assemblies show remnant polarization (Pr) values ranging from 27 to 30 μC cm−2 with concomitant variations in the coercive field (Ec) values at a lower frequency of 0.1 Hz. The observed features for the P–E loop characteristics of all the assemblies are reminiscent of triglycine sulphate (TGS) and certain other supramolecular ferroelectrics. Interestingly, ferroelectric fatigue measurements on all these systems show sizable variations as the cavitands with hard Li+ ions exhibiting the maximum (fatigue) tolerance and the ones with higher polarizable Cs+ ions show a reduction in Pr values up to 35%, after 105 switching cycles. The results signify the effect of encapsulated guest molecules in altering the polarization attributes (Pr, Ec and fatigue tolerance) via host–guest interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...