FeNbSb p-type half-Heusler compound: beneficial thermomechanical properties and high-temperature stability for thermoelectrics
Abstract
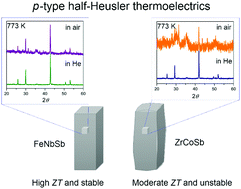
Recently, it has been reported that the FeNbSb p-type half-Heusler compound exhibits exceptionally high thermoelectric (TE) figure of merit ZT = 1.5 at 1200 K [C. Fu et al., Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 8144]. However, for practical utilization of FeNbSb in TE devices, the thermomechanical properties and high-temperature stability need to be considered. Herein, we synthesized polycrystalline high-density bulk samples of FeNbSb and examined their thermal expansion coefficient, sound velocity, and high-temperature stability. The magnitude of the lattice thermal conductivity was analyzed based on the evaluated physical properties such as the elastic modulus and the Grüneisen parameter. The obtained data were compared with those of the ZrCoSb p-type half-Heusler compound, which had been considered as a good TE material until FeNbSb was investigated. FeNbSb exhibited a thermal expansion coefficient closer to those of n-type half Heusler compounds than ZrCoSb. Furthermore, FeNbSb was more stable than ZrCoSb at high temperatures both in an inert atmosphere and in air. Thus, it can be concluded that FeNbSb is more suitable for p-type half-Heusler TE materials than ZrCoSb from the viewpoint of not only TE properties but also thermomechanical properties and high-temperature stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...