Bio-inspired polydopamine coating as a facile approach to constructing polymer nanocomposites for energy storage†
Abstract
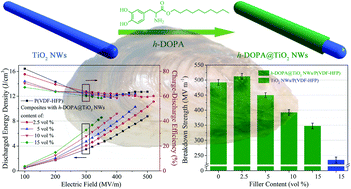
The attractiveness of dielectric polymer nanocomposites stems from their potential applications in electrical insulation and energy storage devices. However, the inevitable electrical mismatch and incompatibility between nanofillers and polymer matrices usually give rise to undesirable dielectric properties and weak energy storage capability. Despite the progress achieved to date, there is still plenty of room for further improvement in terms of energy storage of polymer nanocomposites. Herein, anatase TiO2 nanowires (NWs) were utilized as dopants into a ferroelectric polymer since their moderate dielectric constant is beneficial for alleviating the electric field intensification in the polymer–filler system. Besides, inspired by the strong adhesion property of mussels, a brush-like long-chain tailed dopamine derivative (h-DOPA) is employed to improve the inclusion of TiO2 NWs into the polymer matrix, leading to remarkably reduced dielectric loss and leakage current densities in comparison with the nanocomposites with raw nanowires. Benefiting from the excellent compatibility between these two components, the breakdown strength of these proposed nanocomposites decreases gently from ca. 520 MV m−1 to ca. 350 MV m−1, accompanied by nanofiller loadings from 2.5 vol% to 15 vol%. Moreover, the nanocomposite with 2.5 vol% h-DOPA@TiO2 NWs discharges an ultrahigh energy storage density of 11.13 J cm−3 at 520 MV m−1, while that of the pure polymer can reach only up to 8.75 J cm−3 at 500 MV m−1. A strikingly high energy density of 8.57 J cm−3 is also achieved with the nanofiller volume fraction as high as 15% at a low electric field of 350 MV m−1, nearly double that of pure P(VDF-HFP) (4.76 J cm−3 at 360 MV m−1). The results and methods presented here provide deep insights into a facile and versatile approach to fabricate polymer nanocomposites with high energy storage capability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...