Nanoscale interfacial electroactivity in PVDF/PVDF-TrFE blended films with enhanced dielectric and ferroelectric properties†
Abstract
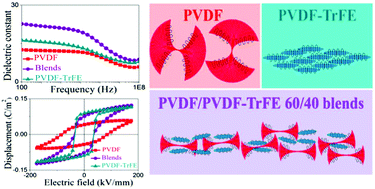
The typical limitations of ferroelectric polymers like poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) – low crystallinity and indirect ferroelectric β-phase crystallization – and poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) (PVDF-TrFE) – high materials and processing costs and a low Curie point – are tackled by a simple and industrially viable melt blending approach. Despite the immiscible nature of PVDF and PVDF-TrFE, strong interactions exist between the two polymers, which substantially affect the morphology and texture of the blends as well as their dielectric and ferroelectric properties. Surprisingly, minor amounts of PVDF-TrFE lead to a significant increase in the β-phase content and preferred orientation of PVDF, well beyond the rule-of-mixtures. Moreover, the blends exhibit maximum increases in the dielectric constant of 80% and 30%, respectively, compared with pure PVDF and PVDF-TrFE. The ferroelectric remnant polarization increases from 0.040 to 0.077 C m−2, while the coercive field decreases from 75 to 32 kV mm−1 with increasing PVDF-TrFE content from 0 to 40 wt%. The enhancement of properties is explained by the strong interactions at the interfaces between PVDF and PVDF-TrFE, which also suppress the Curie transition of PVDF-TrFE, providing a potentially increased working temperature range for blended films, which is important in applications like non-volatile energy storage devices, ferroelectric field-effect transistors and touch sensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...