NIR-I-to-NIR-II fluorescent nanomaterials for biomedical imaging and cancer therapy
Abstract
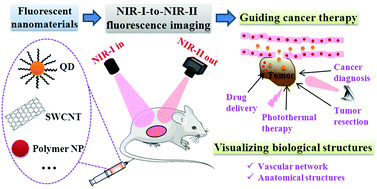
Near-infrared (NIR) fluorescence imaging, which affords high imaging resolution owing to deep tissue penetration of NIR photons, is an attractive imaging modality for both biomedical research and clinical applications. To further improve the image contrast at increased tissue depth, recently much attention has been focused on the development of NIR-I-to-NIR-II fluorescence imaging, which can remarkably reduce the interference from photon absorption, scattering and tissue autofluorescence with excitation in the 700–950 nm NIR-I window and emission in the 1000–1700 nm NIR-II window. In this review, we highlight recently developed NIR-I-to-NIR-II fluorescent nanomaterials, including silver chalcogenide quantum dots, single-walled carbon nanotubes and polymer nanoparticles. We discuss the advantages of these nanomaterials as fluorescent tags in deep tissue imaging by comparing them with conventional fluorophores, and then survey the implementation of NIR fluorescence imaging with these nanomaterials, including instrumentation, data analysis and surface biofunctionalization of the nanomaterials. Finally, we discuss recent applications of NIR-I-to-NIR-II fluorescent nanomaterials in the biomedical imaging field, with an emphasis on how to use them to achieve simultaneous cancer diagnosis and therapy.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...