An efficient strategy to synthesize a multifunctional ferroferric oxide core@dye/SiO2@Au shell nanocomposite and its targeted tumor theranostics†
Abstract
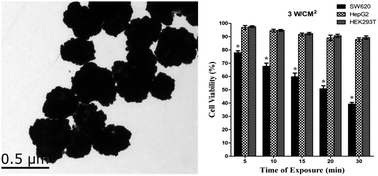
Magnetic nanoparticles with superparamagnetic properties have provided a versatile platform for constructing multifunctional nanostructures, which show great promise in tumor-targeted multimodal imaging and non-invasive therapy. Herein, we first systematically investigated the effect of crystalline water in the reactants on the assembly of primary Fe3O4 nanocrystals prepared by a solvothermal method. The presence of water would hinder the formation of monodisperse Fe3O4 nanocrystals. The regular spheric Fe3O4 nanoclusters with high saturated magnetization values and superparamagnetism can be synthesized with anhydrous reactants and sodium citrate as a stabilizer. Furthermore, the monodisperse Fe3O4 nanoclusters were used as cores and coated with fluorescent dye molecule covalently-doped silica layers, on which carbohydrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles could be assembled. Fe3O4 core@dye/SiO2@Au shell nanocomposites were gradually formed by several cycles of a reduction process in the growth solution. The resultant ferroferric oxide@dye/silica@Au nanoshells exhibited good biocompatibility, an excellent T2-weighted relaxation rate, a strong fluorescence signal and tunable near IR surface plasmon resonance (SPR) spectra. Finally, colorectal cancer cell SW620-specific phage fusion proteins (fusion-pVIII) were conjugated onto the surface of gold nanoshells, which exhibited a maximal SPR peak of 774 nm and effectively achieved the photothermal ablation of tumor cells selectively with 808 nm laser irradiation for 10 min in a light intensity of 3 W cm−2. Additionally, the prepared bio-nanocomposite showed good T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Therefore, the Fe3O4@dye/SiO2@Au@fusion-pVIII nanocomposites were successfully prepared and applied for targeted optical imaging and the targeted photothermal therapy of cancer cells. The prepared bio-nanocomposites can be potentially applied as ideal contrast agents for tumors in MRI.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...