In vitro and in vivo combined antibacterial effect of levofloxacin/silver co-loaded electrospun fibrous membranes
Abstract
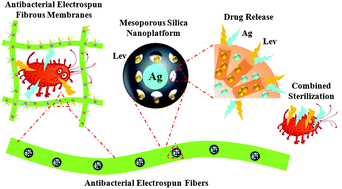
Post-surgery mesh infections are one of the most common complications of hernia repair at the interface of implant materials and tissue, because high doses of antimicrobial agents are toxic and low doses of antibacterial agents are ineffective, with no good clinical solution currently available. To reduce the infection rates after mesh implantation, we designed a “one-pot synthesized” mesoporous silica nanoplatform consisting of levofloxacin (Lev) and silver (Lev@MSN@Ag) composites with poly-L-lactide (PLLA) electrospun fibrous membranes via blending electrospinning. With advances in the combined antibacterial agents Lev and Ag at a low dosage for the treatment of drug-resistant bacterial infections (28 μg mL−1 Lev and 12 μg mL−1 Ag) with a concentration of 5 × 105 CFU mL−1, the composite electrospun fibers act as a carrier for drug-loading and have an antibacterial effect over 8 weeks. Lev@MSN@Ag–PLLA fibers showed a superior antibacterial effect on drug resistant strains in the in vitro test at low doses of antibacterial agents. Further, the in vivo study showed that Lev@MSN@Ag–PLLA fibers significantly inhibited bacterial growth and infection over 8 weeks through the combined effect of low dosage antibacterial drugs. In conclusion, the Lev@MSN@Ag–PLLA fibers provided an advanced combined antibacterial nanoplatform of low dosage for the treatment of drug-resistant bacterial infections.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...